Recently we attended a Future Blockchain hackathon hosted by Deutsche Telekom, and secured the second prize with our solution which solved some of the complex problems associated with Clinical Research Trials. This seemed like a good opportunity to write about our process and describe how we explore new and innovative solutions here at GoSmarten.
Producing new pharmaceutical drugs is a very expensive process. Every new drug needs to go through a number of validation steps before it can be released on the market. One of the most complicated steps is human clinical trials. To be deemed safe and without side effects, a drug has to be tested on volunteers in extremely thorough and well monitored clinical trials.
Our first task was to gain a better understanding of the bigger picture. It is essential to understand the different roles and actors that take part in this ecosystem in order to provide a relevant solution. Only by getting to know the entire chain, can we find a solution that will truly address the problem.
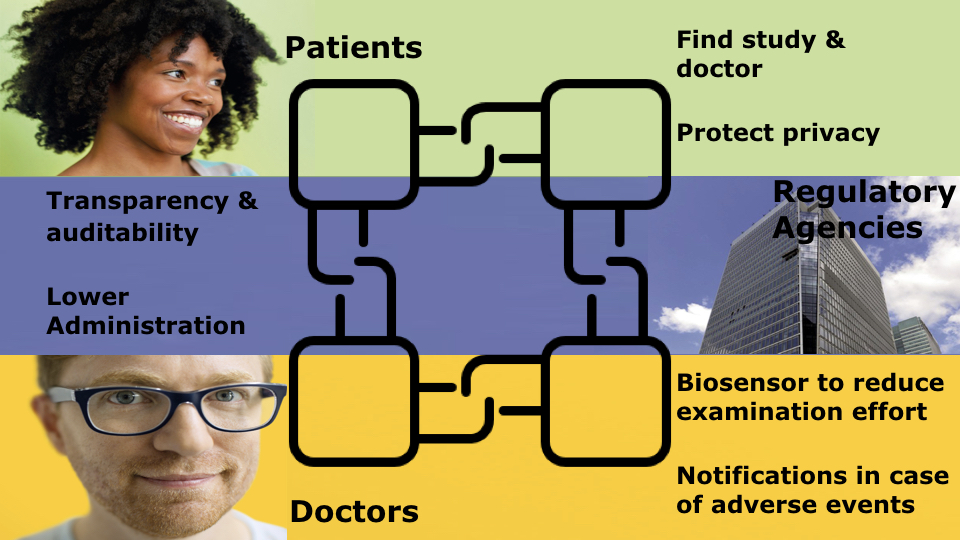
Let’s dive right in with a short description of the ecosystem we worked on. We could identify four different kind of actors:
- Clinical Research Organization (CRO): they research new drugs to cure diseases and help patients. The main problem they face is organizing clinical studies and finding enough suitable volunteers to take part in them.
- Patients/volunteers: our research showed that many of the patients are suffering from terminal diseases. They’ve reached a stage where traditional treatments are not enough and they are looking for an alternative solution in experimental drugs. They are taking their fate into their own hands and are actively looking for studies that could potentially save their lives. It is completely up to them to find an adequate clinical trial, find out if they are eligible to take part in it, search for nearby hospitals and doctors which conduct the study and enroll in it. This all represents a huge challenge, and is a large reason for the low number of participants in trials.
- Doctors/hospitals: they are the ones on the field conducting the studies and following the required protocols. It is extremely time consuming and involves a lot of paperwork, with little rewards for the doctors.
- Regulatory agencies: they are overseeing the trials and need to thoroughly validate the protocols and ensure that they are followed at every stage of a trial.
Now that we better understand all of the stakeholders that are involved, we need to investigate exactly how they interact with each other.
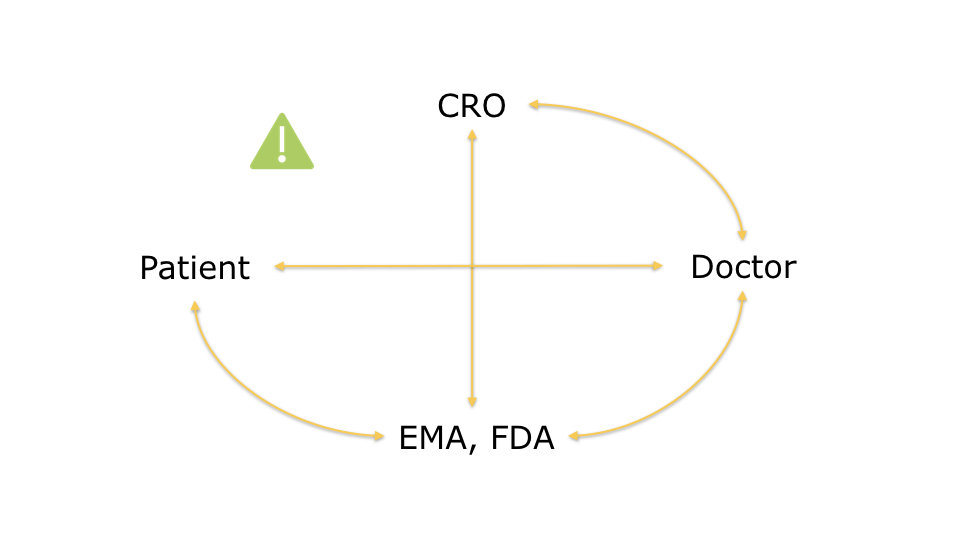
A key aspect of the relationships in this ecosystem is that CROs initiate the clinical trials but have very
little control over them. The doctors are the ones who conduct the studies and interact with the patients.
CROs must never know who the patients are to prevent any risk of fraud.
Doctors can only share some anonymised information with the CROs, such as the number of participants involved
and the overall progress of the study. Patient confidentiality can never be compromised.
On the other hand, the regulatory agencies, such as FDA in the USA or EMA in the EU, must have complete access to the overall documentation so that they can validate the study and ensure that the protocols were correctly applied.
After identifying the different actors and their relationships, we can now start crafting a plan which will solve some of the bottlenecks involved in running clinical research trials, and in that way increase patient participation.
We decided to use Hyperledger Fabric for its ability to implement a safe and scalable private blockchain solution . Hyperledger Fabric gives us the ability to have a common ledger for all participants to store high level transactions and sub-networks with more restrictive access which will safeguard sensitive patient data. You can learn more about the technical aspects of Hyperledger in our other article about effective blockchain solutions for businesses .
After successfully implementing a blockchain based data storage layer, we turned our attention to the frontend web interface. It was clear that an easy and straightforward way was needed for patients to search and apply to trials. For this, we also needed to create interfaces where Clinical Research Organisations could create and monitor their trials, and for doctors to be able to see patient applications, and accept or reject them. Finally, regulatory agencies also needed their own interface where they could easily audit all the data in the system.
Using smart contracts, we could automatically match patients to trials that are relevant to their health condition and put them in contact with the doctors in charge. Once a patient volunteered for a clinical trial and was vetted by a medical practitioner, this automatically generated a sub-channel for their exchanges. With this, we managed to achieve complete patient data confidentiality and safety.
Because we use blockchain, we can guarantee the authenticity of every transaction that occurs, and generate a strong audit trail, thus greatly simplifying the work of regulatory agencies. Auditing clinical trials can now be faster and a lot safer, reducing the time to market for drugs that could potentially save millions of lives.
At this point, our solution is already complete and manages to successfully solve all the main problems that were presented to us regarding Clinical Research Trials. However, all the research we gathered showed us that it was possible to even further innovate and streamline the process of trials for doctors and hospitals, who still face large time investments when conducting them.
Administrating the drugs is only the tip of the iceberg. Doctors have to conduct regular follow-ups and health checks with the volunteers, in addition to paperwork duties. So we came to the idea of using state of the art IoT sensors currently being developed by Merck, which would allow us to monitor and automatically log the presence of certain chemicals in a patient's blood. This can ensure that patients regularly administer the correct dosage of the drug being tested, while also raising an alert to the hospital in case of an adverse reaction. When used in conjunction with smart contracts, these IoT sensors can validate that the clinical trial protocol is being followed as specified, which could even further decrease necessary auditing and paperwork.
Crafting and then implementing a solution in two days to a complex problem such as clinical research trials, a topic we knew nothing about before this hackathon, proved quite fun as well as challenging. We managed to demonstrate that blockchain is not just another buzzword technology, but can be quite successfully used in the medical and pharmaceutical industry in order to increase transparency, reduce bureaucracy, strengthen process adherence, and most importantly, save lives.
If you’ve enjoyed reading this article, feel free to get in touch with us at hello@gosmarten.com.